Darth Vader-Inspired Sea Monster Discovered Near Vietnam
Matthew Russell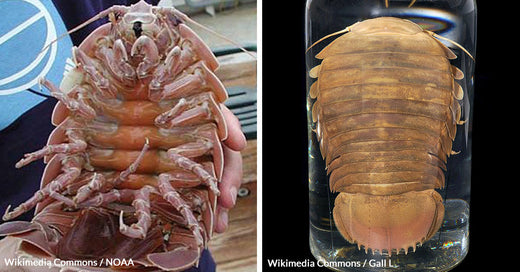
The ocean's depths continue to unveil astonishing secrets, with the latest revelation being a colossal sea bug christened after one of cinema's most notorious villains.
Scientists have identified a new species, Bathynomus vaderi, aptly named for its Darth Vader-like head, marking a significant addition to marine biodiversity.
Discovery and Naming
In 2022, researchers from Hanoi University acquired several deep-sea isopods from a local market in Quy Nhơn City, Vietnam. Among these specimens was an unfamiliar species that had eluded scientific classification until now. Carcinologist Peter Ng from the National University of Singapore led the team that formally described this novel sea bug in a paper published by ZooKeys.
The species was named Bathynomus vaderi because its carapace closely resembles the iconic helmet of Darth Vader from the Star Wars saga, as ScienceAlert reports.

Photo: Wikimedia Commons / NOAA, License: Public Domain
A new species of giant sea bug, Bathynomus vaderi, has been discovered in Vietnam.
Physical Characteristics
Bathynomus vaderi measures between 260 to 280 millimeters in length and weighs over a kilogram, positioning it as a supergiant among its relatives. This species boasts a wide, rectangular clypeal region with parallel lateral margins and a narrowly acute apex. Additionally, it features 11 upwardly curved pleotelson spines and a set of prickly setae that enhance its formidable appearance.
Despite its intimidating size and appearance, B. vaderi poses no threat to humans, primarily feeding on decaying organic matter found on the ocean floor, according to ScienceAlert.
Habitat and Behavior
This newly identified species inhabits the deep waters near the Spratly Islands in the South China Sea. Bathynomus vaderi exemplifies deep-sea gigantism, a phenomenon where deep-dwelling creatures grow significantly larger than their shallow-water counterparts.
As Forbes reports, this adaptation likely aids in energy storage in nutrient-scarce environments, allowing them to thrive in the abyssal zones. The sea bug scavenges for carcasses and may also prey on live organisms, playing a crucial role in the marine ecosystem.

Photo: Wikimedia Commons / Gall L (2019). Invertebrate Zoology Division, Yale Peabody Museum. Yale University Peabody Museum, License: Public Domain
The sea bug is named after Darth Vader due to its helmet-like head.
Culinary Significance
In recent years, Bathynomus vaderi has surged in popularity as a delicacy in Vietnam. Seafood markets in cities like Hanoi, Hồ Chí Minh City, and Đà Nẵng City now regularly display these giant sea bugs in chilled tanks, catering to both local consumers and high-end restaurants. The demand surged around 2017, transforming Bathynomus from a low-value bycatch to a sought-after menu feature, fetching prices of approximately US$40 per kilogram.
According to Forbes, the transition of B. vaderi into the culinary scene underscores the growing trend of exotic seafood in Vietnam.
Conservation and Environmental Impact
The rise in popularity of B. vaderi has raised significant concerns regarding sustainable harvesting practices. Increased fishing efforts, coupled with the expansion of deep-sea mining for minerals, oil, and gas, pose substantial threats to the fragile deep-sea ecosystems.
Experts emphasize the urgent need for comprehensive research to understand the species’ distribution, population dynamics, and ecological role to prevent overexploitation and ensure the long-term survival of these enigmatic creatures. As EurekAlert reports, sustainable practices are paramount to balance commercial interests with ecological preservation.

Photo: Wikimedia Commons / Gall L (2019). Invertebrate Zoology Division, Yale Peabody Museum. Yale University Peabody Museum, License: Public Domain
This species weighs over a kilogram, classifying it as a supergiant isopod.
Future Research and Implications
The discovery of Bathynomus vaderi underscores the vast unknowns that still exist within our oceans. As researchers continue to explore and document marine biodiversity, each new species offers valuable insights into the complexity and resilience of underwater ecosystems. Protecting these environments is paramount, especially as human activities penetrate deeper into the ocean’s abyssal zones.
This finding serves as a reminder of the importance of sustainable practices and the need to balance commercial interests with ecological preservation. The scientific community remains committed to furthering our understanding of deep-sea life forms, ensuring that future generations can continue to marvel at the mysteries of the ocean.
